Abstract
Background
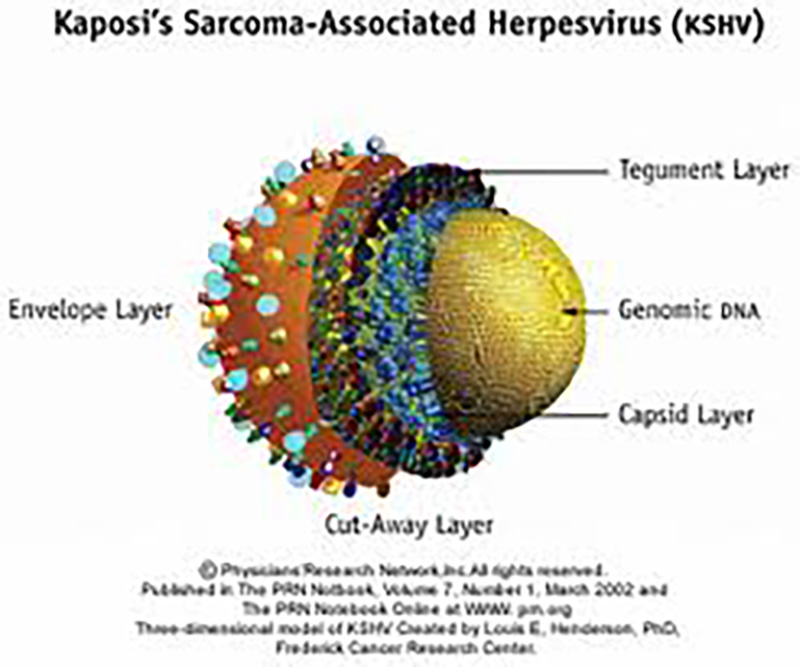
KSHV is a tumorigenic γ-herpesvirus that has been identified as the etiologic agent of Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS), a multifocal highly vascularized neoplasm that is the most common malignancy associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). The virus encodes a constitutively active chemokine receptor homologue, vGPCR that possesses potent angiogenic and tumorigenic properties, and is critical for KSHV pathobiology. To date, a number of signaling pathways have been identified as key in mediating vGPCR oncogenic potential.
Findings
In this study, we identify a novel pathway, the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which is dysregulated by vGPCR expression in endothelial cells. Expression of vGPCR in endothelial cells enhances the nuclear accumulation of β-catenin, that correlates with an increase in β-catenin transcriptional activity. Activation of β-catenin signaling by vGPCR is dependent on the PI3K/Akt pathway, as treatment of vGPCR-expressing cells with a pharmacological inhibitor of PI3K, leads to a decreased activation of a β-catenin-driven reporter, a significant decrease in expression of β-catenin target genes, and reduced endothelial tube formation.
Conclusions
Given the critical role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis, the findings from this study suggest a novel mechanism in KSHV-induced malignancies.
The electronic version of this article is the complete one and can be found online
at: http://www.virologyj.com/content/11/1/218